输入示例
在本教程中,将为大家分享IdeaXR的 输入事件 系统捕获玩家输入。您的应用可以使用多种不同类型的输入——键盘, 游戏手柄, 鼠标等等。本章节将向您展示一些最常见的场景, 您也可以将其作为您自己项目的起点。
tip
要想了解IdeaXR的输入系统是如何工作的,请参阅使用InputEvent。
事件和轮询
在开发应用的时候,您可能会想让您的程序对某一输入事件作出反应,例如按下 "跳跃" 按钮。在其他情况下, 您可能希望只要有一个键被按下就会发生一些事情,比如移动。在第一种情况下, 您可以使用 _input() 函数, 只要有输入事件发生就会调用该函数。 在第二种情况下,IdeaXR提供了 Input 单例, 您可以用它来查询一个输入的状态。
func _input(event):
if event.is_action_pressed("jump"):
jump()
func _physics_process(delta):
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
# Move as long as the key/button is pressed.
position.x += speed * delta
这使您能够灵活地混合和匹配所执行输入的处理类型。对于本教程的其余部分, 我们将专注于使用 _input () 捕捉单个事件。
输入
输入事件是继承自 输入事件 的对象。根据事件类型,对象将包含与该事件相关的特定属性。为了了解事件的实际情况, 添加一个节点并附加以下脚本:
extends Node
func _input(event):
print(event.as_text())
当按下按键,移动鼠标,并执行其他输入,您会在输出窗口中看到每个事件滚动。下面是输出窗口打印日志的一个示例:
A
InputEventMouseMotion : button_mask=0, position=(108, 108), relative=(26, 1), speed=(164.152496, 159.119843), pressure=(0), tilt=(0, 0)
InputEventMouseButton : button_index=BUTTON_LEFT, pressed=true, position=(108, 107), button_mask=1, doubleclick=false
InputEventMouseButton : button_index=BUTTON_LEFT, pressed=false, position=(108, 107), button_mask=0, doubleclick=false
S
F
Alt
InputEventMouseMotion : button_mask=0, position=(108, 107), relative=(0, -1), speed=(164.152496, 159.119843), pressure=(0), tilt=(0, 0)
如您所见,对于不同类型的输入,结果是非常不同的。按键事件甚至被打印为按键符号。例如,让我们考虑 鼠标按钮输入事件 。 它继承自以下类:
- InputEvent - 所有输入事件的基类
- InputEventWithModifiers - 增加了检查是否按下修饰按键,如
Shift或Alt - InputEventMouse - 增加鼠标事件属性,如
position - 鼠标按钮输入事件 - 包含按下的按钮的索引,无论是双击,或是其他
info
在处理事件时,建议打开类引用,这样可以检查事件类型的可用属性和方法。
如果您尝试访问不包含属性的输入类型上的属性,则可能会遇到错误。例如,对 InputEventKey 调用 Position 。要避免这种情况,请确保首先测试事件类型:
func _input(event):
if event is InputEventMouseButton:
print("mouse button event at ", event.position)
InputMap
事件表 是处理各种输入的最灵活的方法. 您可以通过创建命名的输入 动作 来使用它,可以为它分配任意数量的输入事件,例如按键或鼠标点击。 一个新的IdeaXR项目已经包含许多默认定义操作。
您可以通过编辑->项目设置->键位映射了解下默认的事件类型,然后再根据应用开发的实际需要进行扩充。
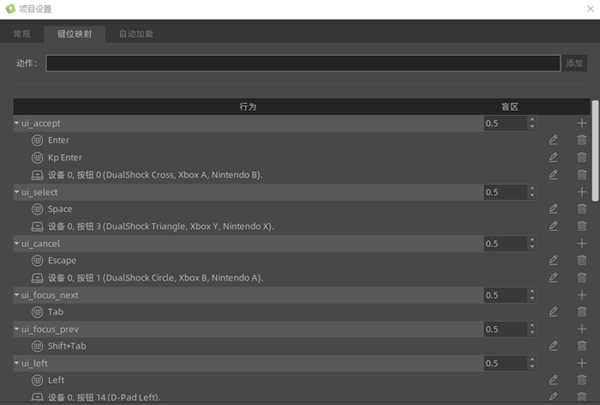
捕捉动作
一旦您在上面的 键位映射 中定义了动作, 可以在脚本中使用 is_action_pressed() 和 is_action_released() 处理它们。通过名称查找响应的动作:
func _input(event):
if event.is_action_pressed("my_action"):
print("my_action occurred!")
键盘事件
键盘事件在 InputEventKey 中被捕获。虽然建议使用输入动作来代替,但在某些情况下,你可能会想专门查看按键事件,对于当前示例, 来检查一下 T :
func _input(event):
if event is InputEventKey and event.pressed:
if event.scancode == KEY_T:
print("T was pressed")
注意
由于键盘冲突,如果您一次性按下了太多的键,那么在特定时间点,可能是无法将所有按键输入都进行注册的。根据按键在键盘上位置的不同,某些按键产生冲突的可能性会比其他的要高。
组合按键
修饰键属性继承自 InputEventWithModifiers ,可使用布尔属性检查修饰键的组合。试想,如果需要在按下 T 时发生一件事,而按下 Shift + T 时发生不同的事:
func _input(event):
if event is InputEventKey and event.pressed:
if event.scancode == KEY_T:
if event.shift:
print("Shift+T was pressed")
else:
print("T was pressed")
鼠标事件
鼠标事件继承自 InputEventMouse 并被分成 InputEventMouseButton 和 InputEventMouseMotion 两种类型。注意,这意味着所有鼠标事件都包含 position 属性。
鼠标按钮
捕获鼠标按钮与处理按键事件非常相似。ButtonList 包含每个可能按钮的 BUTTON_* 常量列表,它将在事件的 button_index 属性中报告。注意,鼠标滚轮也可以算作一个按钮——准确地说是两个按钮,滚轮键 BUTTON_WHEEL_UP和 BUTTON_WHEEL_DOWN 都是独立的事件,均可以被事件系统捕获到。
func _input(event):
if event is InputEventMouseButton:
if event.button_index == BUTTON_LEFT and event.pressed:
print("Left button was clicked at ", event.position)
if event.button_index == BUTTON_WHEEL_UP and event.pressed:
print("Wheel up")
鼠标移动
InputEventMouseMotion 只要鼠标移动就会发生事件. 可以通过 relative 属性找到移动的距离.
下面是一个使用鼠标事件拖放 Sprite 节点的例子:
extends Node
var dragging = false
var click_radius = 32 # Size of the sprite.
func _input(event):
if event is InputEventMouseButton and event.button_index == BUTTON_LEFT:
if (event.position - $Sprite.position).length() < click_radius:
# Start dragging if the click is on the sprite.
if not dragging and event.pressed:
dragging = true
# Stop dragging if the button is released.
if dragging and not event.pressed:
dragging = false
if event is InputEventMouseMotion and dragging:
# While dragging, move the sprite with the mouse.
$Sprite.position = event.position
触摸事件
如果你使用的是触摸屏设备,就可以生成触摸事件。InputEventScreenTouch 相当于鼠标点击事件,而 InputEventScreenDrag 的工作原理与鼠标移动一致。
小技巧
要在非触摸屏设备上测试触摸事件,请打开 “项目设置”,进入 “Input Devices/Pointing” (输入设备/触点)部分。启用 “Emulate Touch From Mouse”(根据鼠标模拟触摸),您的项目将把鼠标单击和移动解释为触摸事件。